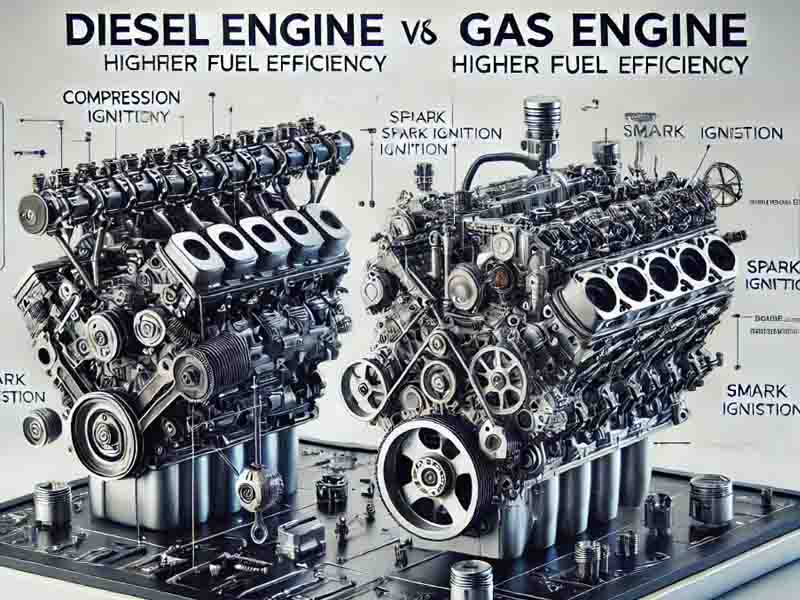
Dieselspecialists – Key Insights into diesel engines begin with understanding their combustion process. Unlike gas engines, which rely on a spark plug to ignite the air-fuel mixture, diesel engines use compression ignition. Air is compressed to a high temperature, and fuel is injected directly into the cylinder, causing spontaneous combustion. This process makes diesel engines more fuel-efficient and powerful, making them ideal for heavy-duty vehicles and machinery.
One of the key advantages of compression ignition is its efficiency. Diesel engines extract more energy from fuel compared to gas engines, which waste energy in heat dissipation. However, this also means diesel engines operate at higher pressures, requiring stronger components and a robust cooling system to maintain performance and longevity.
Key Insights into the differences between diesel and gas engines reveal significant contrasts in their operation and performance. Gas engines operate using a spark-ignition system, where a spark plug ignites a pre-mixed combination of air and fuel. This results in a smoother and quieter operation, making gas engines preferable for passenger cars and motorcycles.
“Motorcycles in Malaysia: Adventure & Touring Experiences”
On the other hand, diesel engines deliver more torque at lower RPMs, which enhances their ability to handle heavy loads. This is why diesel engines are commonly found in trucks, buses, and industrial machinery. Additionally, diesel fuel has a higher energy density than gasoline, contributing to better fuel economy. However, diesel engines tend to be heavier, more expensive to manufacture, and require specialized maintenance compared to their gas counterparts.
Key Insights into diesel and gas engines also include their environmental impact and efficiency. Diesel engines generally have better fuel efficiency, consuming less fuel per mile compared to gas engines. This advantage makes them a preferred choice for long-haul transportation and commercial applications.
However, diesel engines produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which contribute to air pollution. Modern diesel engines are now equipped with advanced emission control systems, such as diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR), to meet stricter environmental regulations.
Meanwhile, gas engines produce lower NOx emissions but consume more fuel over time. With the rise of electric and hybrid alternatives, both diesel and gas engines are evolving to become cleaner and more sustainable. Future innovations in fuel injection systems, turbocharging, and biofuels may further improve their efficiency and environmental footprint.
Understanding these key insights into diesel and gas engines helps consumers and industry professionals make informed decisions based on efficiency, cost, and environmental considerations.
“Humanoid Robots Now Building Cars in China”
[SITE_NAME] - alternative fuels changing diesel engines are accelerating the evolution of transportation technology as industries shift toward cleaner and…
Diesel Specialists | Expert Engine Solutions for Diesel, Gasoline & More - Diesel particulate filter failures on Komatsu heavy equipment…
Diesel Specialists | Expert Engine Solutions for Diesel, Gasoline & More - A common rail diesel engine significantly enhances fuel…
Diesel Specialists | Expert Engine Solutions for Diesel, Gasoline & More - heavy duty diesel engines different characteristics set them…
Diesel Specialists | Expert Engine Solutions for Diesel, Gasoline & More - Properly inspect your diesel engine before a long…
Diesel Specialists | Expert Engine Solutions for Diesel, Gasoline & More - the role of fuel injector is crucial in…